Hi,Aren't there sysctl(8)s for that?
Code:dev.cpu.0.freq_levels: CPU frequency levels dev.cpu.0.freq: Current CPU frequency
sysctl -a | grep freq returns:kern.timecounter.tc.BCM2835-3.frequency: 1000000
kern.eventtimer.et.BCM2835-3.frequency: 1000000
kern.acct_chkfreq: 15
net.inet.sctp.sack_freq: 2
debug.cpufreq.verbose: 0
debug.cpufreq.lowest: 0
debug.uart_poll_freq: 50 sysctl -a | grep cpu returns:kern.smp.cpus: 1
kern.smp.maxcpus: 1
kern.ccpu: 1948
kern.sched.cpusetsize: 4
kern.pin_pcpu_swi: 0
kern.vt.splash_cpu_duration: 10
kern.vt.splash_cpu_style: 2
kern.vt.splash_ncpu: 0
kern.vt.splash_cpu: 0
vfs.ncpurgeminvnodes: 128
net.inet.tcp.per_cpu_timers: 0
debug.cpufreq.verbose: 0
debug.cpufreq.lowest: 0
hw.ncpu: 1
hw.cpu.quirks.actlr_set: 0
hw.cpu.quirks.actlr_mask: 0
security.jail.param.cpuset.id: 0 dmesg |grep cpu leads somewhere.It returns nothing :/It might be that the cpufreq(4) driver works differently or not at all on armv6.
Maybedmesg |grep cpuleads somewhere.
In case you ask on the arm mailing list, please also tell them which installation image you used.
Hi,If you're looking for config.txt you can find it in /boot/msdos/.
cat command returns:init_uart_clock=3000000
enable_uart=1
kernel=u-boot.bin
kernel7=u-boot.bin
dtoverlay=mmc
Checking now, thanks.
I am not trying to overclock it but I saw that it was running slower than other OS. So I think it's CPU frequency is set to lower in order to prevent heating.I guessed you were looking for it as you need to adjust it in order to overclock the Pi.

Raspberry Pi Documentation - Configuration
The official documentation for Raspberry Pi computers and microcontrollerswww.raspberrypi.org
init_uart_clock=3000000 is the CPU clock (am I right?). But I can't find uart_clock on the link you posted.No, a UART is a serial port. It needs a clock to move data through a shift register at a specific rate. Better not mess around with that one or you may not be able to correctly send/receive data through its serial port.I thinkinit_uart_clock=3000000is the CPU clock (am I right?).
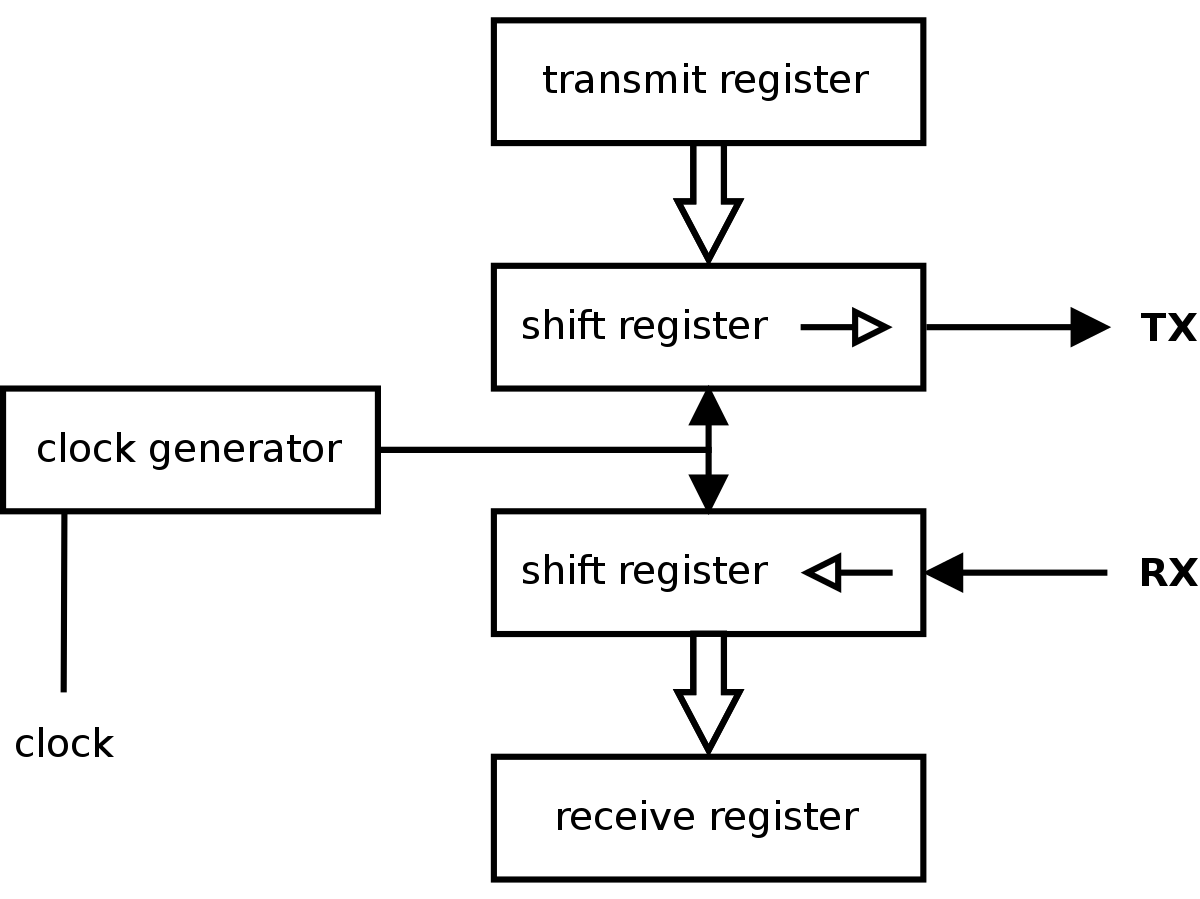
Okay, thank you!No, a UART is a serial port.

Universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter - Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org
powerd_enable="YES" to rc.conf? x_enable="YES" or if_x_enable="YES", I don't think that we can add vi_enable="YES" to start vi at the boot time. I searched net for how to enable powerd in freebsd and a few results show up. None of them directly saying it is powerd_enable="YES", I feel like I need to learn what I can add to rc.conf.ifconfig_* variables are for InterFaces, like the ethernet or wireless interfaces, it directly translates to the ifconfig(8) command. foo_enable is generally used to enable services, the command service -e will show you which services have been enabled. Services are started with scripts in /etc/rc.d and /usr/local/etc/rc.d. Those *_enable variables just tells the system which ones to activate.sshd_enable="YES" causes /etc/rc.d/sshd to be executed during boot which starts the sshd(8) daemon.Thank you so much!Theifconfig_*variables are for InterFaces, like the ethernet or wireless interfaces, it directly translates to the ifconfig(8) command.foo_enableis generally used to enable services, the commandservice -ewill show you which services have been enabled. Services are started with scripts in /etc/rc.d and /usr/local/etc/rc.d. Those*_enablevariables just tells the system which ones to activate.
For example,sshd_enable="YES"causes /etc/rc.d/sshd to be executed during boot which starts the sshd(8) daemon.
